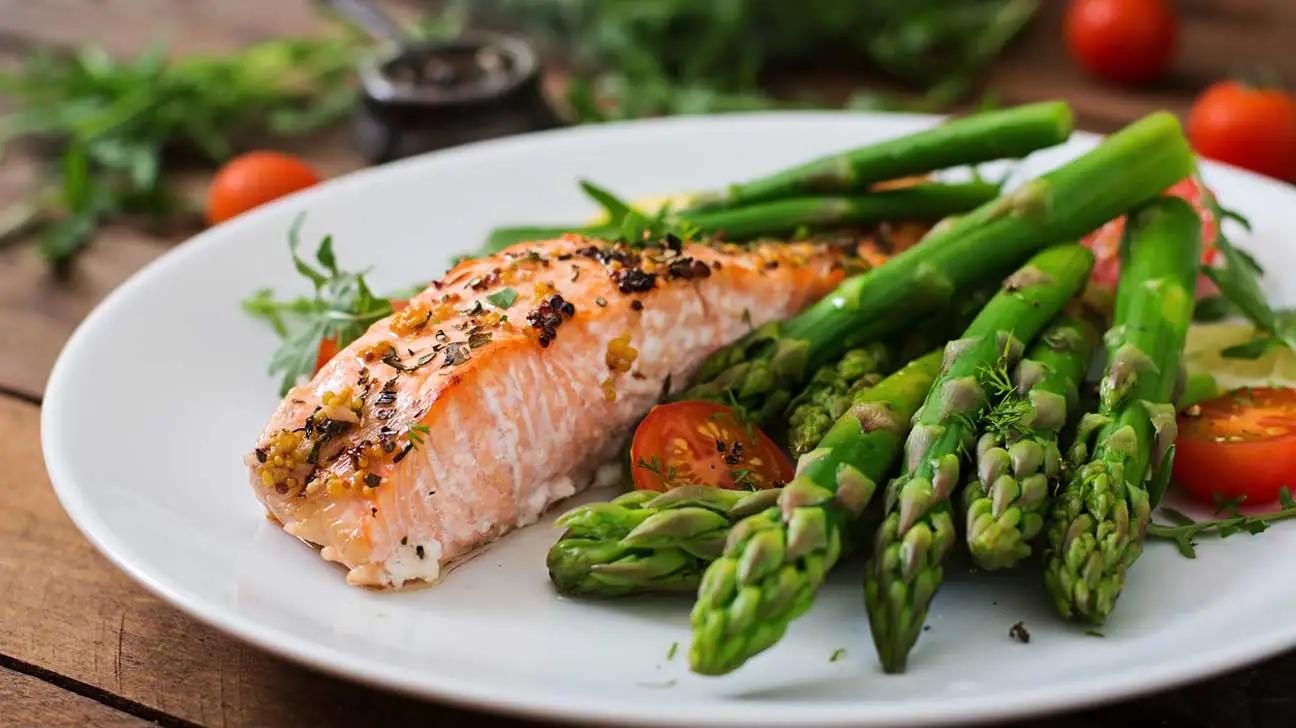
Diet meals refer to any food or beverage that has been altered to reduce its fat, sugar and/or carbohydrate content. They’re commonly used as a means of weight loss but may also be beneficial if you want to build muscle mass.
Before embarking on any new diet, be sure to consult with your doctor first. This is especially important if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are the main energy source for your body, made up of sugars, starches or fibers found in many foods like grains, dairy and fruits.
Sugar is the simplest form of carbohydrates and it naturally occurs in fresh produce like fruit, vegetables and milk. Unfortunately, it’s also added to many processed foods like candies and sodas for added sweetness.
Refined sugars provide calories, but lack essential vitamins, minerals and fiber that may contribute to weight gain. Eating foods like whole grains, fruits and vegetables instead can provide you with essential nutrients without adding added sugars.
Proteins
Protein is an essential building block of your body. Not only does it repair cells, build muscle mass and provide energy for daily tasks, but protein also plays a major role in cell repair processes.
Maintaining an optimal level of protein in your diet is essential for everyone. Make sure to get enough to keep muscles and bones strong, but not so much that you become overfed or dehydrated.
Your ideal protein-packed diet meal consists of multiple sources of the nutrient. These may include lean meats, low-fat dairy, poultry or fish as well as some plant-based proteins.
Fats
Fats give foods a rich, satisfying texture and flavor. Furthermore, they supply essential fatty acids your body requires for growth and development.
Additionally, fats help the body absorb essential vitamins and minerals. But too much fat can lead to weight gain as well as health problems like heart disease.
Saturated fats are commonly found in meat, butter, dairy products, tropical plant-based oils and highly processed foods. Excess saturated fat can increase your blood cholesterol and put you at greater risk for heart disease.
Unsaturated fats (monounsaturated and polyunsaturated) are primarily found in vegetables, nuts and fish. At room temperature these unsaturated fats remain liquid; however when refrigerated they solidify.
Monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats have been known to lower your blood cholesterol and decrease the risk of heart disease, while saturated and trans fats are detrimental for health.
Vegetables
Vegetables are an integral part of a balanced diet, providing essential nutrients like fiber, vitamins and minerals.
Eating vegetables as part of your daily diet can help you shed pounds and maintain them. Vegetables are low in calories, have a high water content, and contain plenty of antioxidants to support weight loss efforts.
They provide a significant amount of fiber, which may help you feel satiated and reduce your appetite.
Vegetables are divided into five subgroups according to their nutrient content: dark green vegetables, red and orange veggies, starchy veggies and legumes (beans and peas). Eating a variety of veggies ensures you get all the essential vitamins and minerals.
Fruits
Fruits are an integral part of a nutritious diet. Not only do they supply essential vitamins and minerals, but they’re also high in fiber for added bonus points!
Fruit-rich diets may reduce your risk for chronic illnesses like heart disease, cancer and diabetes. The amount of fruit recommended daily depends on your age, gender, height and weight.
Fruits are also an excellent source of dietary fiber, vitamin C and potassium. These essential nutrients can promote good health and help build a robust immune system.






 The Essential Guide to Digestive Enzymes Australia: Boost Your Gut Health
The Essential Guide to Digestive Enzymes Australia: Boost Your Gut Health  Latest Breakthroughs in Acne Treatment
Latest Breakthroughs in Acne Treatment  The Rise of Virtual Fitness Classes
The Rise of Virtual Fitness Classes  Fun and Creative Ways to Stay Active Indoors
Fun and Creative Ways to Stay Active Indoors  Linking Oral Health to Overall Wellbeing
Linking Oral Health to Overall Wellbeing  Can You Exercise While Pregnant?
Can You Exercise While Pregnant?  Is Skin Cancer Curable?
Is Skin Cancer Curable?  How Much Is Dental Bonding?
How Much Is Dental Bonding?  The Rise of Telemedicine and Its Impact on Healthcare
The Rise of Telemedicine and Its Impact on Healthcare 